In today’s world, the textile and fashion industries are facing a significant crisis of textile waste. This waste not only poses economic challenges but also has a severe impact on the environment.
Let’s talk about the economic aspect. Take China as an example. Despite being the largest producer of textiles globally, the recycling rate of textile waste is relatively low. In 2022, less than 20% of the 26 billion kg of textile waste was recycled. Similarly, in the EU, only about a quarter of the 16 billion kg of textile waste produced annually is recycled, with the rest being disposed of in landfills.
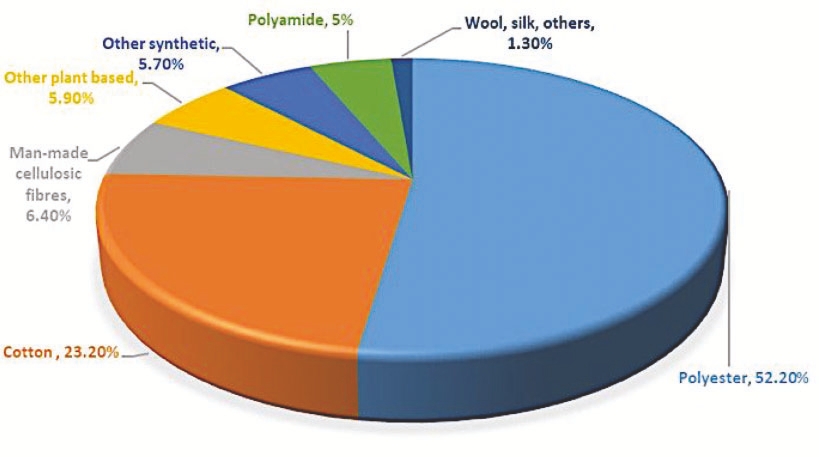
Now, let’s look at the environmental effects. The production of textiles consumes a vast amount of resources and generates a large amount of waste. For instance, the fashion industry is one of the biggest consumers and polluters of water. The production of 1 kg of cotton, equivalent to one T-shirt and one pair of jeans, requires an excessive amount of water. Additionally, the textile industry is a major contributor to carbon dioxide emissions and chemical pollution.
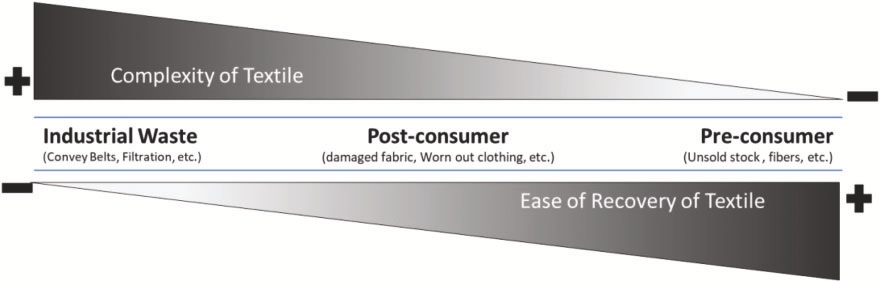
However, there are solutions. Textile reuse and recycling are becoming increasingly popular. Reuse is more beneficial than recycling, as it extends the useful life of textile products. Textile recycling can be classified into several categories, such as upcycling, downcycling, closed-loop, and open-loop recycling. Each type plays a vital role in reducing waste.
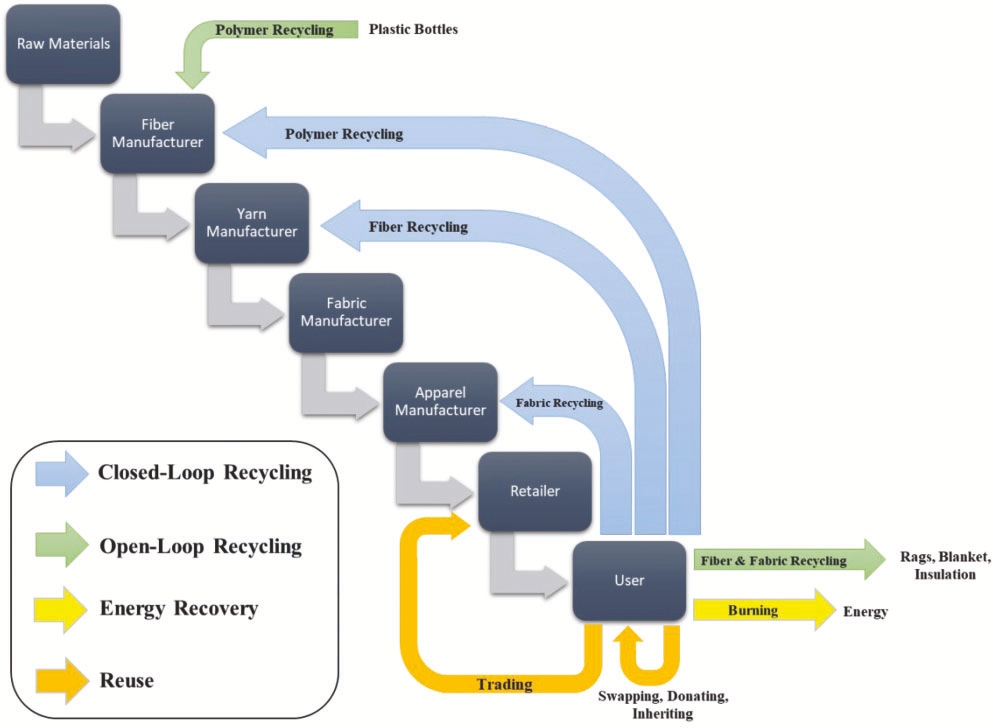
In conclusion, the textile waste problem is a significant challenge, but through increased awareness and the implementation of sustainable practices like reuse and recycling, we can make a positive impact on the environment and move towards a more sustainable future.





